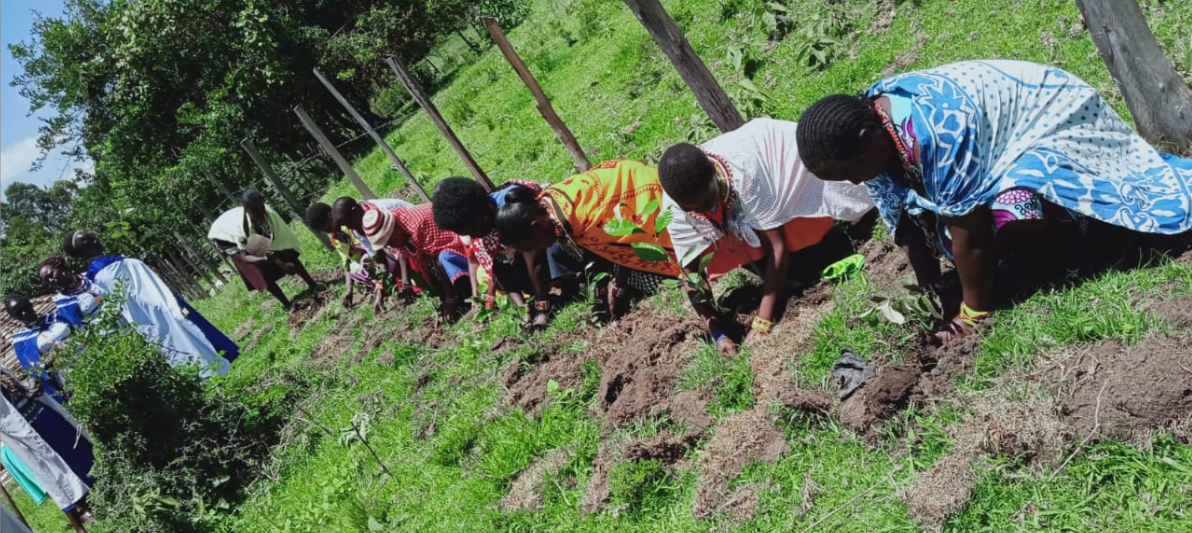
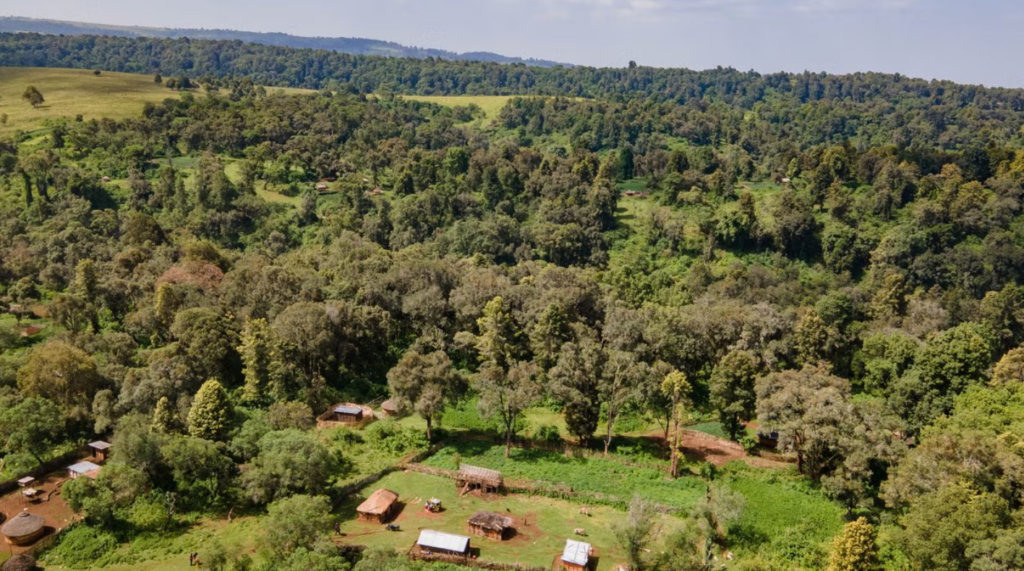
Community-led conservation refers to a re-imaging of conservation as a primarily locally driven action where indigenous peoples and local communities take the lead in managing natural resources, caring for their lands and resources and sustaining their own cultures.
By investing in, and supporting, community-led conservation initiatives and enhancing community capacity to monitor and demonstrate biodiversity outcomes, the project contributes to the base of evidence that demonstrates the crucial role of indigenous peoples and communities in biodiversity conservation and sustainable use.
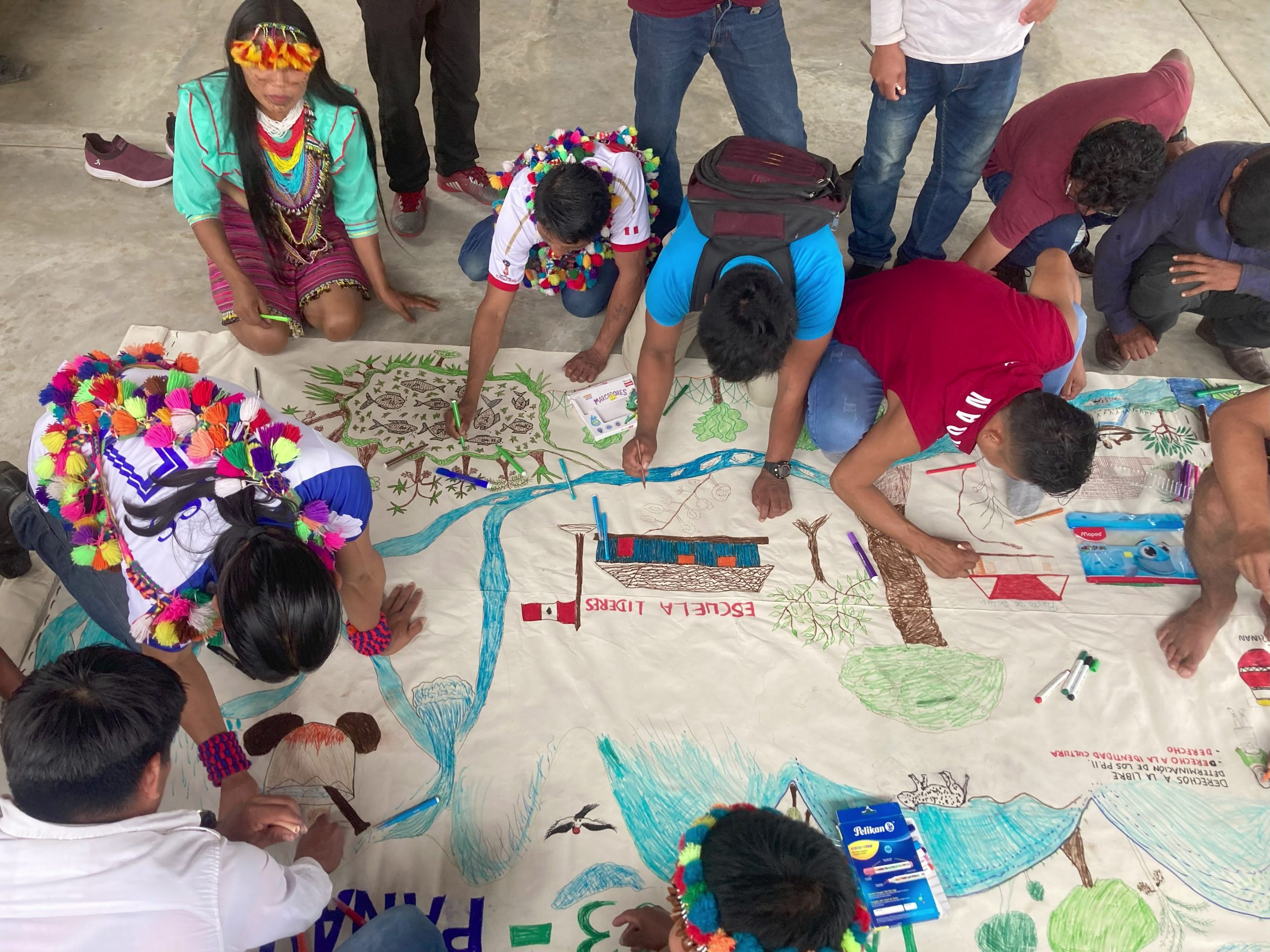

Wampis Nation students drawing the learnings from their leadership training, one of five delivered over a year by LifeMosaic for the Shawi Leadership School in Peru. Photo by Mikey Watts
Further info
Indigenous peoples have developed sophisticated knowledge systems and management practices that have enabled them to live sustainably in their environments for many generations, and in many cases, millennia. By giving them greater control over the management of natural resources, community-led conservation can ensure that these valuable traditions are preserved, and that biodiversity is protected for future generations.
Over the course of the project, this larger base of evidence will directly impact how much local and national governments recognise and support indigenous peoples’ and local communities’ beneficial roles in biodiversity protection. Consequently, this will also improve the level of protection and recognition of their underlying rights to lands, resources and traditional knowledge.
These two aspects of the long-term impact are closely connected: sustaining community-led long-term management of natural resources is linked to the security of underlying tenure, yet in many of the project countries customary tenure is insufficiently recognised.
By demonstrating the valuable contributions that these territories make to national biodiversity priorities, the project makes the case for increasing security of tenure over the longer-term.
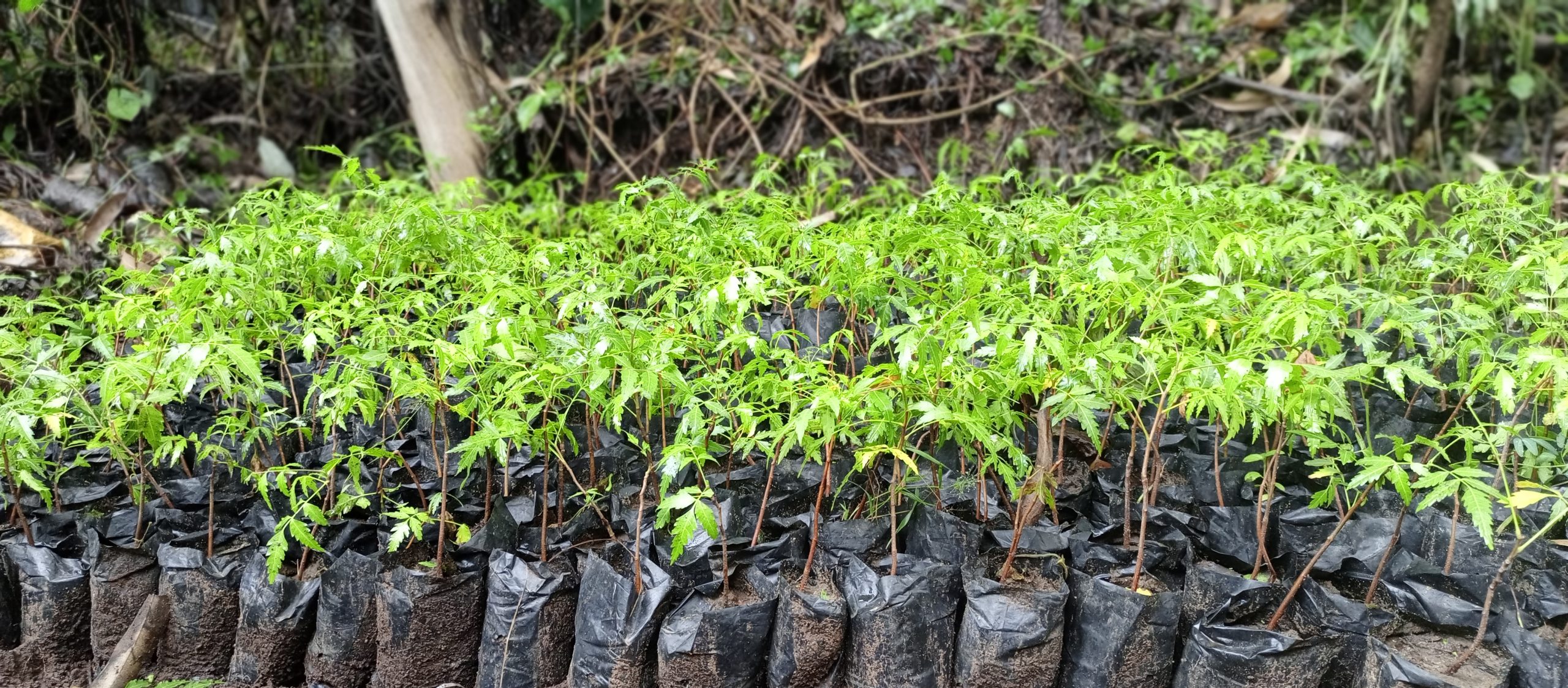

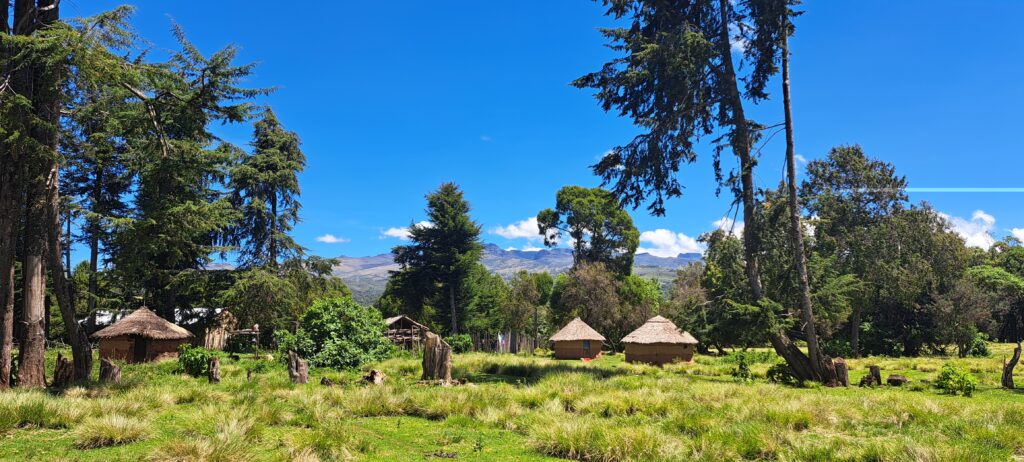
A tree nursery at Olorukoti resource and knowledge center. Photo by IIN.